How to Distinguish male and female rabbit? What is the function of rabbit ear? Do you know, why rabbit has long ear? Do you want to know about rabbits? Find the answer here .
Rabbit Ear Function
1 . Rabbits are animals that are often hunted by other animals. To maintain life, a rabbit using long ears to catch the slightest sound that propagates through the air. For that, the rabbit often enforce ears and move to the right - left - front - rear to collect sounds from all directions. When the rabbit catch the sound of the coming enemy from a distance, then the rabbit will run away and hide quickly .
2 . Rabbit ears also serves to keep the body temperature to stay cool because rabbits can not sweat. In the rabbit ears there are many small blood vessels, so that when they ran the air flowing around the ear will take the heat from existing blood vessels in the ear and cool it. Then the cool blood flow throughout the rabbit body.
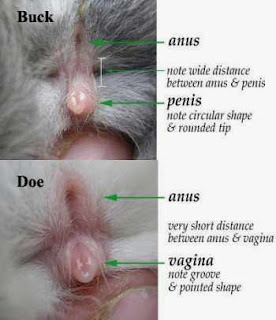
How to Distinguish Male and Female rabbit
Look at this image:
[image: the difference of male and female rabbits - male female rabbit parts
Scientific Facts of Rabbit
Rabbits are mammals of the family Leporidae, which can be found in many parts of the earth. Formerly, these animals are wild animals that live in Africa and Europe. In 1912, rabbits are classified in the order Lagomorpha. Order is divided into two families, namely Ochtonidae ( kind of clever pika whistling ) and Leporidae (including rabbits and hares types ). In Sumatra there is a native species of the Sumatran rabbit ( Nesolagus netscheri ) newly discovered in 1972. In Indonesia there are many local rabbit, the Java rabbit ( Lepus negricollis ) and Sumatra rabbit ( Nesolagus netseherischlgel ). Java rabbit is expected to remain there in the forests around the area of West Java. Bronze feathers blackish brown color. Its tail is orange with a black tip. The weight of adult java rabbit can reach 4 kg. While the Sumatran Rabbit, is the only one of rabbit native to Indonesia. Their Habitat is forests in mountainous of Sumatra island. Body length reaches 40 cm. Yellowish gray- brown fur color .
Biological Data of Rabbit
Life period : 5-10 years
Production period : 1-3 years
Pregnant Period : 28-35 days (average 29-31 days )
Weaning period : 6-8 weeks
Adult Age : 4-10 months
Mated Age : 6-12 months
Mating period after birth ( calving interval ) : 1 week after the child is weaned.
Sex Cycle : Poliestrus. 5 times pregnant in a year
Estrus cycle : Approximately 2 weeks
Estrus period : 11-15 days
Ovulation : Occurs on mating day ( 9-13 hours later )
Fertility : 1-2 hours after mating
Number of births : 4-10 tail (average 6-8 )
Blood volume : 40 ml / kg body weight
Weight of adults : It varies, depending on race, gender, and maintenance factors
Scientific Classification of Rabbit
Kingdom: Animalia
Superphylum: Chordata
Phylum: Vertebrates
Class: Mammalia
Order: Lagomorpha
Family: Leporidae
Rabbit Ear Function
1 . Rabbits are animals that are often hunted by other animals. To maintain life, a rabbit using long ears to catch the slightest sound that propagates through the air. For that, the rabbit often enforce ears and move to the right - left - front - rear to collect sounds from all directions. When the rabbit catch the sound of the coming enemy from a distance, then the rabbit will run away and hide quickly .
2 . Rabbit ears also serves to keep the body temperature to stay cool because rabbits can not sweat. In the rabbit ears there are many small blood vessels, so that when they ran the air flowing around the ear will take the heat from existing blood vessels in the ear and cool it. Then the cool blood flow throughout the rabbit body.
How to Distinguish Male and Female rabbit
Look at this image:
Scientific Facts of Rabbit
Rabbits are mammals of the family Leporidae, which can be found in many parts of the earth. Formerly, these animals are wild animals that live in Africa and Europe. In 1912, rabbits are classified in the order Lagomorpha. Order is divided into two families, namely Ochtonidae ( kind of clever pika whistling ) and Leporidae (including rabbits and hares types ). In Sumatra there is a native species of the Sumatran rabbit ( Nesolagus netscheri ) newly discovered in 1972. In Indonesia there are many local rabbit, the Java rabbit ( Lepus negricollis ) and Sumatra rabbit ( Nesolagus netseherischlgel ). Java rabbit is expected to remain there in the forests around the area of West Java. Bronze feathers blackish brown color. Its tail is orange with a black tip. The weight of adult java rabbit can reach 4 kg. While the Sumatran Rabbit, is the only one of rabbit native to Indonesia. Their Habitat is forests in mountainous of Sumatra island. Body length reaches 40 cm. Yellowish gray- brown fur color .
Biological Data of Rabbit
Life period : 5-10 years
Production period : 1-3 years
Pregnant Period : 28-35 days (average 29-31 days )
Weaning period : 6-8 weeks
Adult Age : 4-10 months
Mated Age : 6-12 months
Mating period after birth ( calving interval ) : 1 week after the child is weaned.
Sex Cycle : Poliestrus. 5 times pregnant in a year
Estrus cycle : Approximately 2 weeks
Estrus period : 11-15 days
Ovulation : Occurs on mating day ( 9-13 hours later )
Fertility : 1-2 hours after mating
Number of births : 4-10 tail (average 6-8 )
Blood volume : 40 ml / kg body weight
Weight of adults : It varies, depending on race, gender, and maintenance factors
Scientific Classification of Rabbit
Kingdom: Animalia
Superphylum: Chordata
Phylum: Vertebrates
Class: Mammalia
Order: Lagomorpha
Family: Leporidae